Differential pressure control valve is a kind of valve, which makes use of the pressure change of medium itself to adjust itself to keep the pressure difference of the controlled system unchanged. Differential pressure valve plays the role of the branch road, automatic regulation of household, elimination of heat network and hydraulic imbalance.
Accurate and stable pressure difference control;
20-250Kpa Pressure difference control range;
Simple debugging, without complex electrical installation;
Long life and durability.
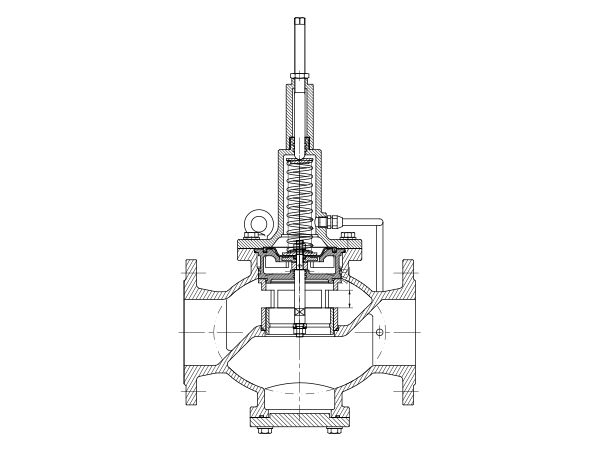
P1 is the pressure of water supply, P2 is the pressure of backwater in the valve and P3 is the pressure of backwater outside the valve. When P1-P3 increases, the induction diaphragm moves the disc upward, reducing the flow area and increasing P2-P3, thereby maintaining P1-P2 constant, i.e. the pressure difference on the control system remains unchanged. Conversely, if P1-P3 decreases, the disc will move down, P2-P3 will decrease, and P1-P2 will remain unchanged. If P1-P3 remains unchanged, and the resistance within the controlled system changes, such as P1-P2 increases, the disc opens slightly, so that P2 returns to its original value, that is, P1-P2 remains unchanged. Therefore, this valve can adjust the pressure changes in the system outside the controlled system.
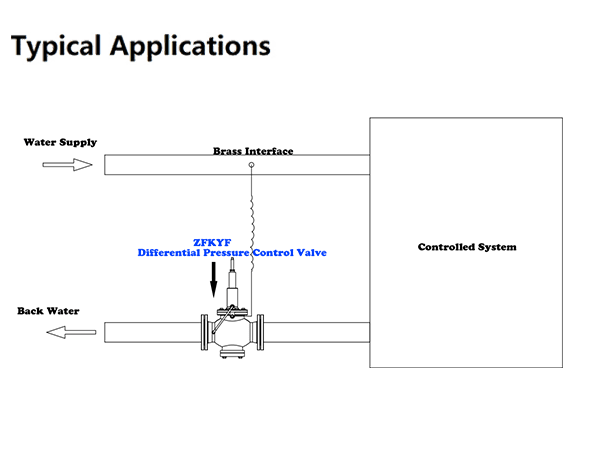
Differential pressure control valve is the backwater installation method. The control pipe is connected with the connection of the water supply pipe. External type: connected with the supply pipe at the front end of the controlled system and connected with the preset control interface of the copper guide valve at the end; The pressure difference control valve and balance valve are used together. The balance valve is responsible for flow measurement, shutoff, and connection of the pressure pipe. For specific use, please consult ZECO Valve Group.
Size Range: 2"~12"
Pressure Rating: 10bar ~ 25bar
Face to Face Dimensions: AMSE B16.10, EN558-1
Flange End Dimension: AMSE B16.1/16.42, AS4087, EN1092-2
Coating: Fusion Bonded Epoxy Coating
Inspection and Test: ISO 5208 / EN 12226-2
Part | Material | Standard |
Body | Ductile Iron | EN 1563/DIN 1693 |
Bonnet | Ductile Iron + C37000 | EN 1563/EN12167 |
Trim | Stainless Steel 431 | EN10088-1/ASTM A959 |
Seat | Stainless Steel 431 | EN10088-1/ASTM A959 |
Diaphragm | EPDM / NBR | ISO 4633 |
Spring | Stainless Steel 431 | EN10088-1/ASTM A959 |
For the materials options not listed, consult factory. ZECO manufactures valves in more than 50 different alloys. | ||
